Hyperthyroidism In Cats Prognosis

Since thyroid hormone regulates most body processes too much production of the hormone causes dramatic clinical changes in the body.
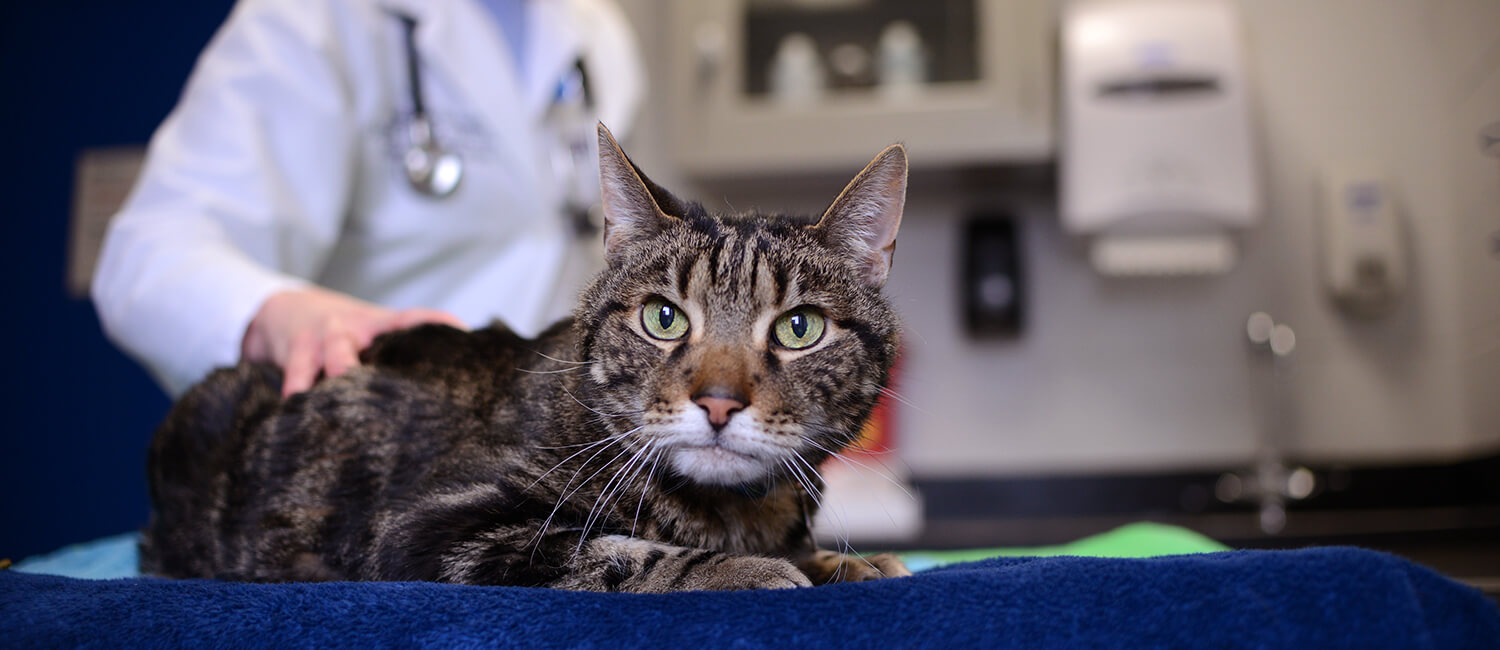
Hyperthyroidism in cats prognosis. Heart rate and rhythm are also assessed as some cats with hyperthyroidism develop secondary cardiac problems. If hyperthyroidism in cats is left untreated the disease will progress and will eventually result in death. Your veterinarian will also ask about your cats appetite and note if theres been weight loss and how rapidly it occurred.
Left untreated hyperthyroidism can result in heart failure and. If left untreated the condition can be fatal. Symptoms tend to develop slowly but hyperthyroidism is serious and can be fatal if left untreated.
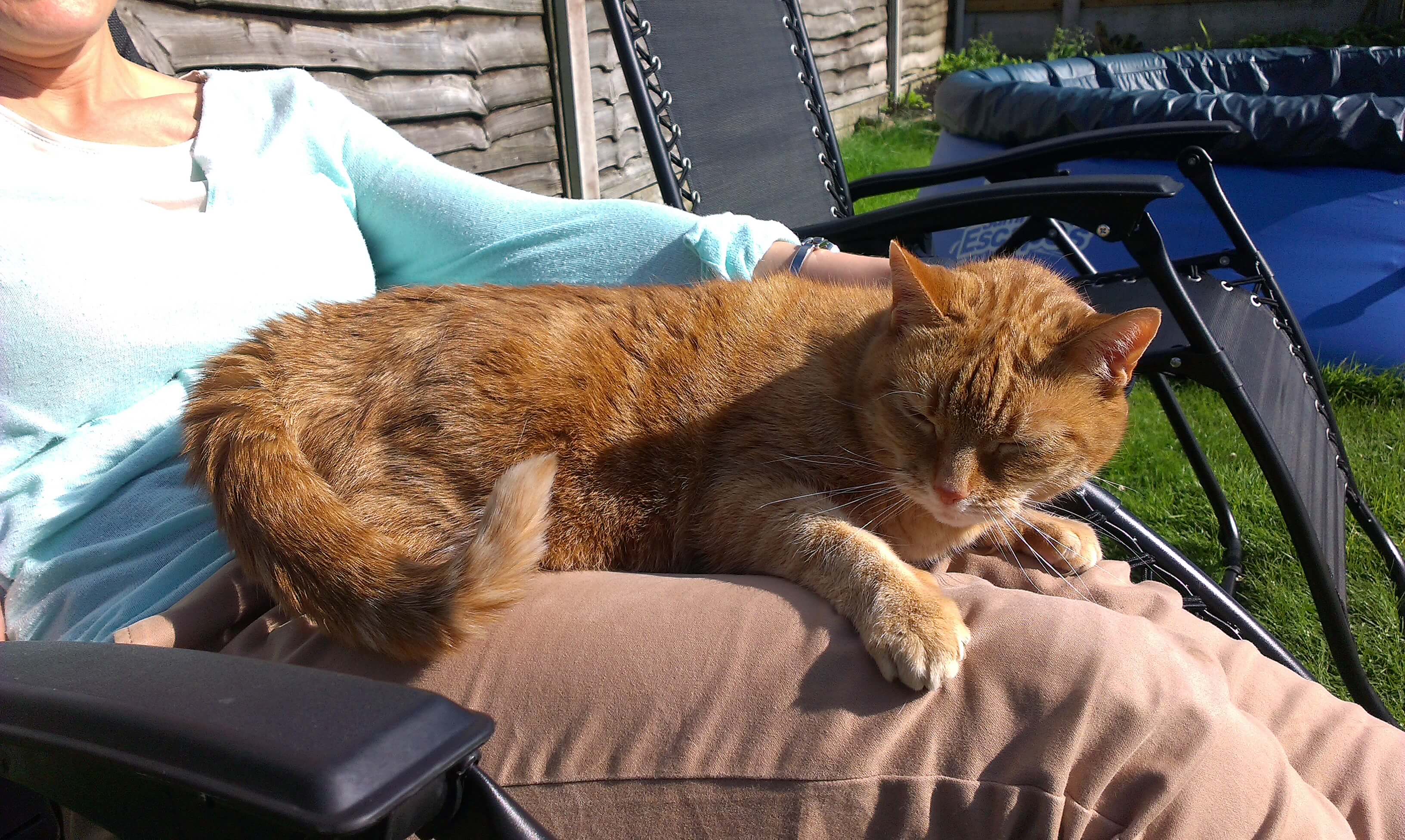
They eat like crazy yet still lose weight. Excessive thirst Increased urination Decreased activity levels. The prognosis of cats with hyperthyroidism may depend on several factors such as.
Typical signs of hyperthyroidism in cats include rapid weight loss rapid heart rate and increased hunger Dr. The cat will experience severe weight loss even if eating regularly or more than usual and are at risk of developing serious secondary conditions such as hypertension high blood pressure and thyrotoxic cardiomyopathy a form of heart disease. Hyperthyroidism is the most common hormone abnormality in cats which is a form of overactive thyroid glands resulting in the overproduction of thyroid hormone.
More specific information on what to expect when your cat is treated with radioactive-iodine therapy at Cornell can be found here. Hypothyroidism is a common condition among humans and dogs but it rarely ever spontaneously occurs in cats. Feline hyperthyroidism in cats is a lethal complaint of a thyroid gland which usually appears with pain and discomfort.
There are a few different treatment options including radioactive iodine therapy surgical treatment and medication. Most cases of hyperthyroidism stem from benign tumors that form in the gland. Most of the time this condition in cats is a result of over-treatment of hyperthyroidism a disease that occurs more frequently.