Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

Adenosine triphosphate chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
Cellular respiration formula explained. The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. Cellular respiration formula is the collective term for a number of different processes which convert biochemical energy derived from nutrients into a molecule called adenosine triphosphate atp the form of usable chemical energy needed to drive cellular processes. During this activity the students work with a group to discuss the compounds and conditions that need to be present in order.
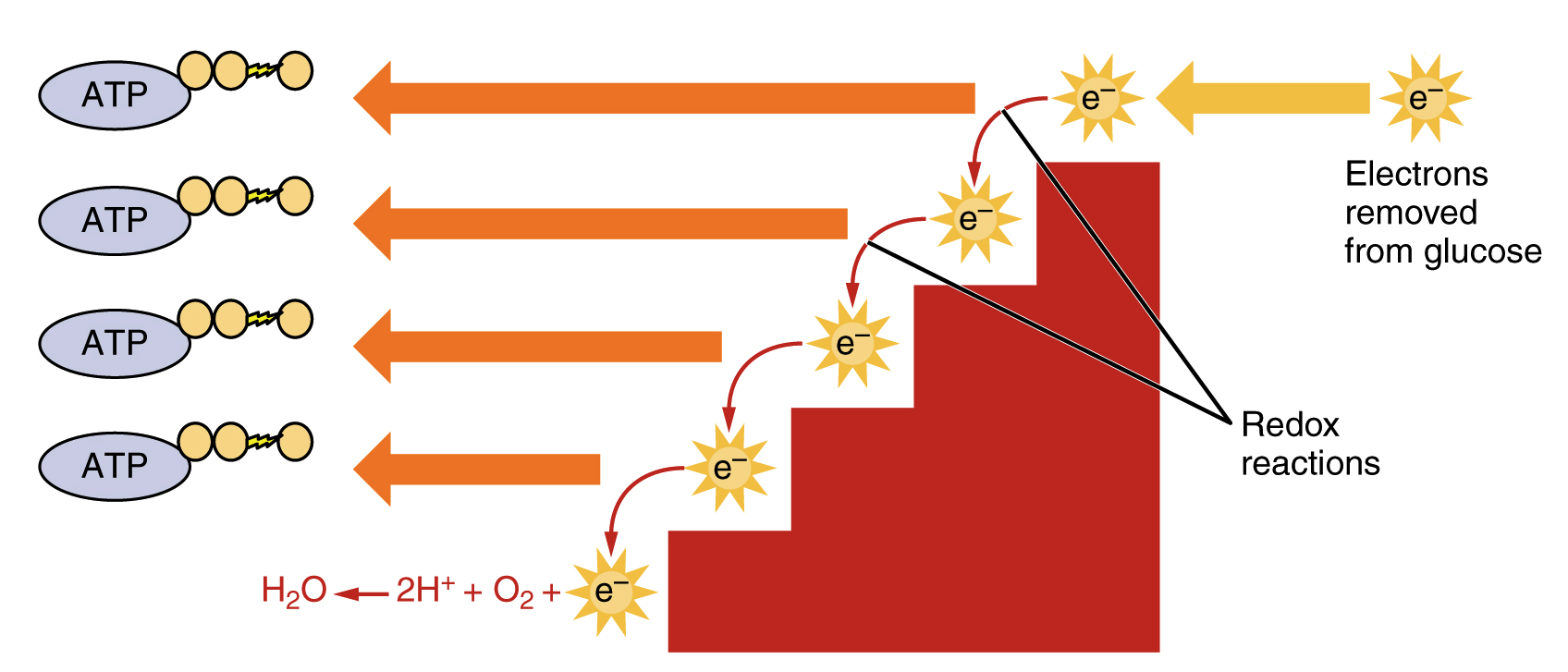
There are two types of electron carriers that are particularly important in cellular respiration. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
The energy released from the broken down molecules are a result of spontaneous catabolic reactions. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. Cellular respiration formula explained.
After reviewing the notes about cellular respiration and fermentation the students turn in the notes they have written either online or on paperThe students then take out their Chromebooks and enter the lab where we work on the fermentation demonstration activity. Such processes are explained below. Cellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP.
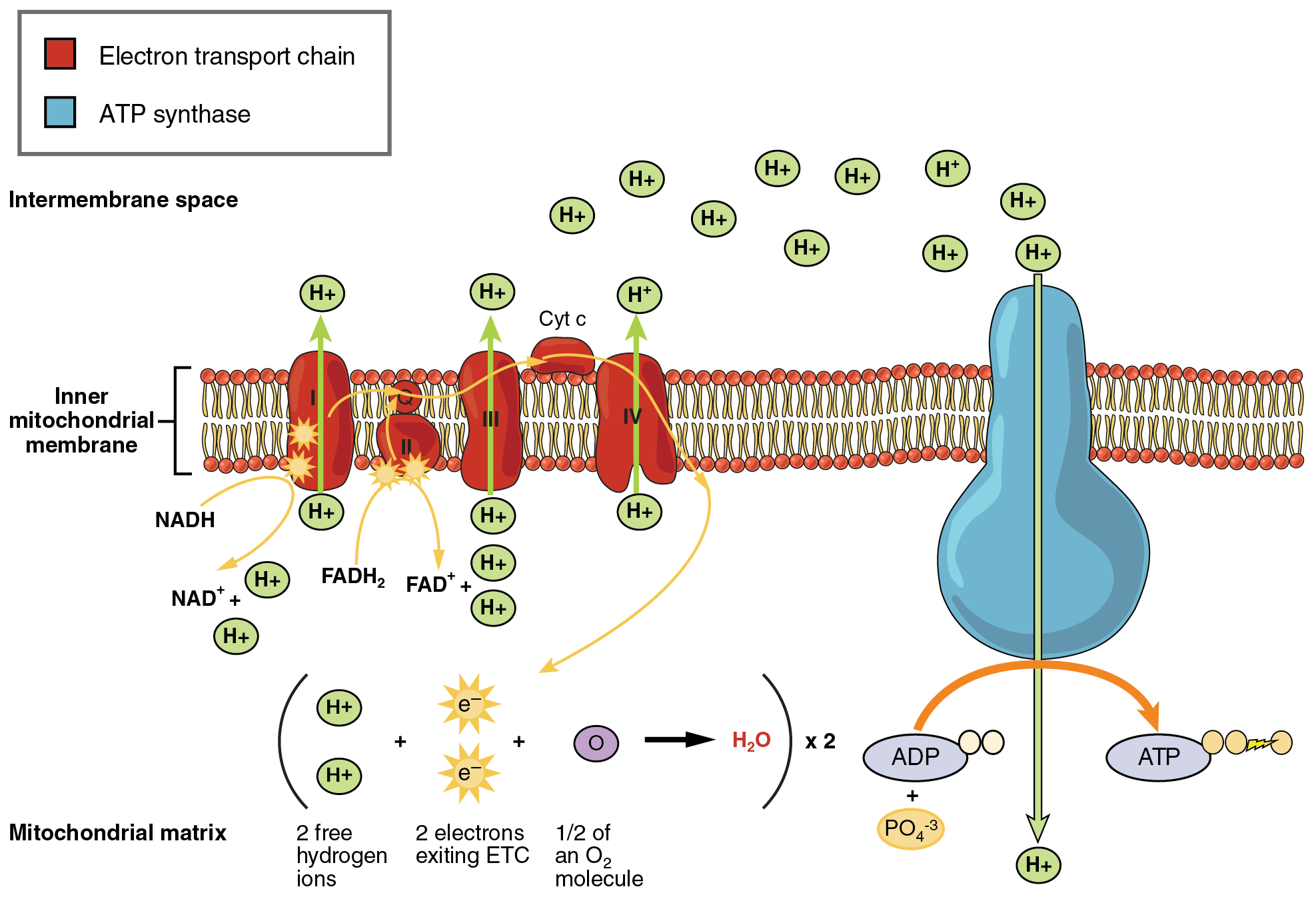
C 6 H 12 O 6 glucose 6O 2 36 ADP depleted ATP 36 P i phosphate groups 6CO 2 6H 2 O 36 ATP. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
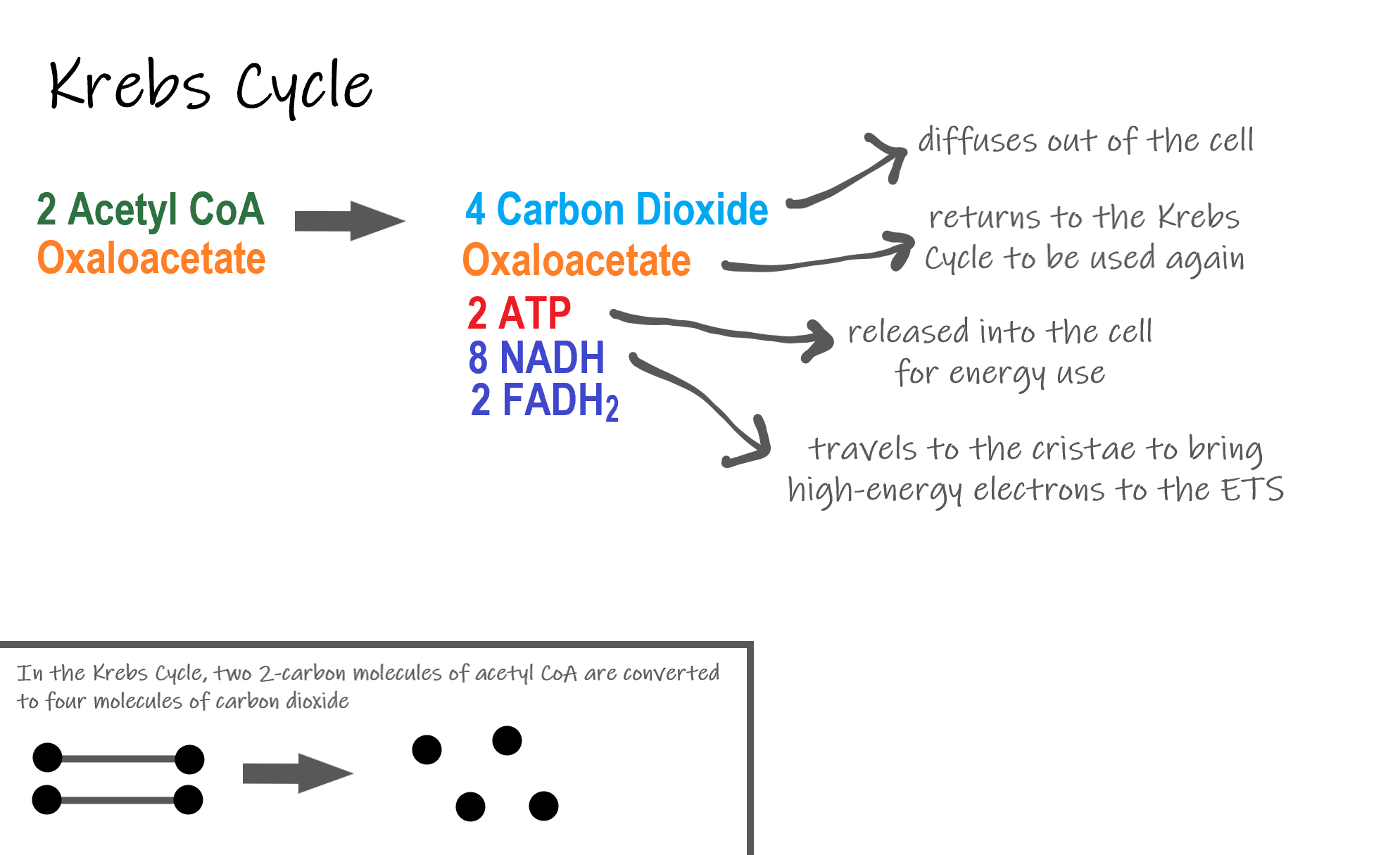
Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy. In summary cellular respiration is a process that cells use to make energy. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.