Cellular Respiration Equation Definition

Cellular Respiration Definition.
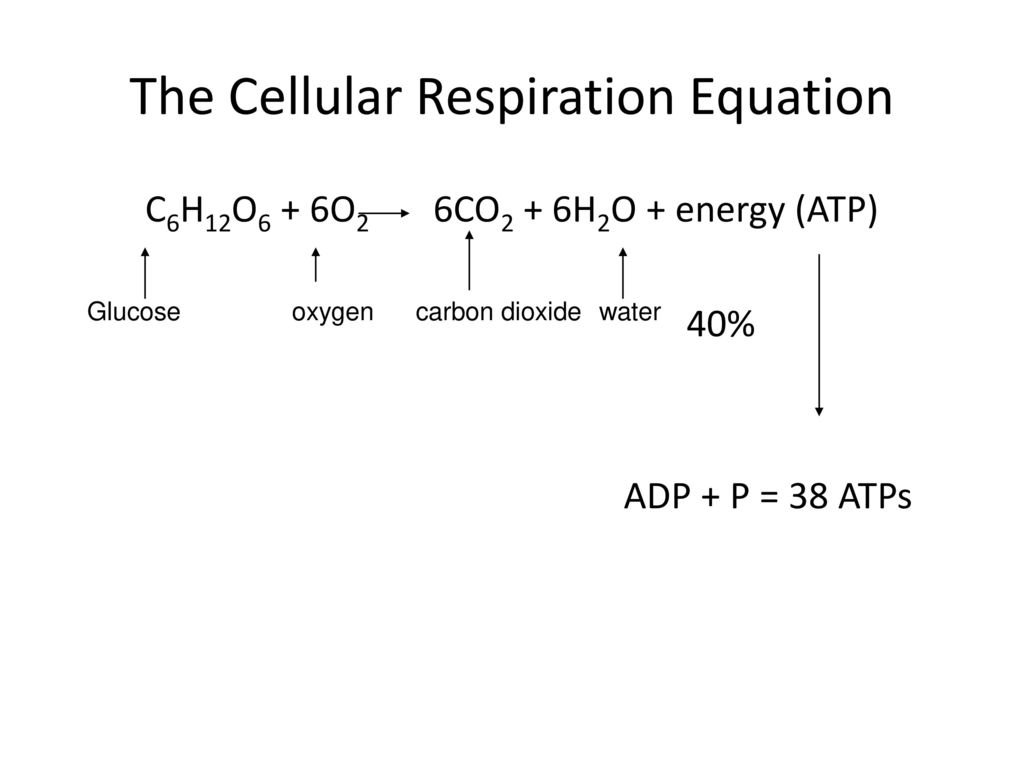
Cellular respiration equation definition. What is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration. Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Cellular respiration is the process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates.
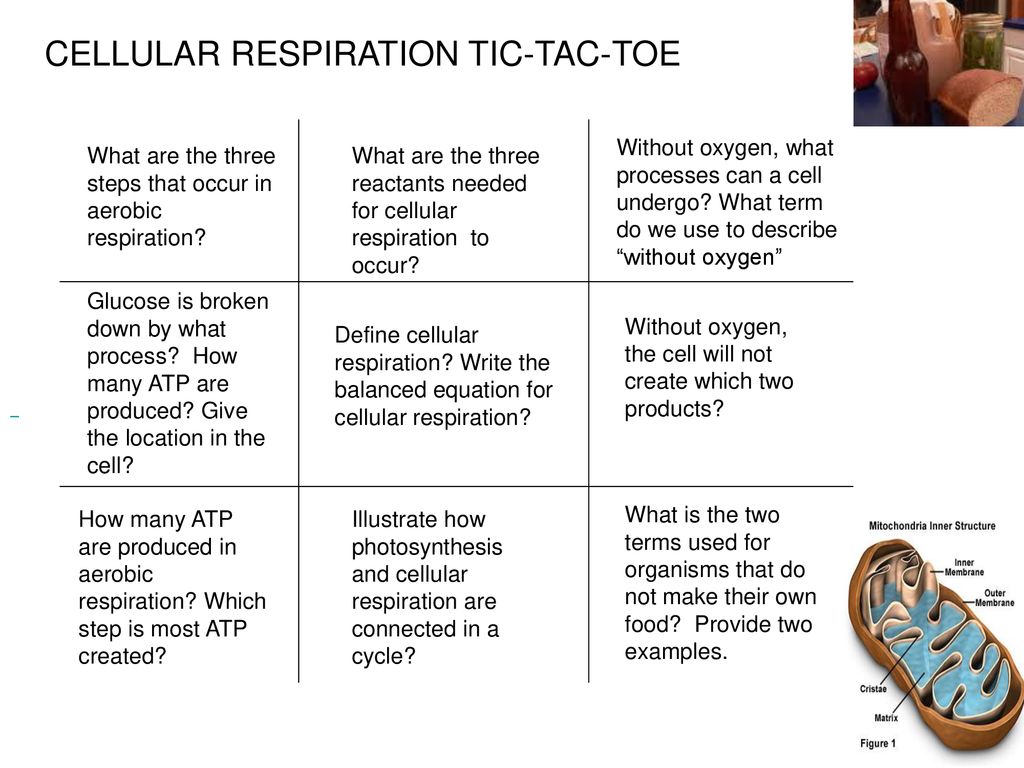
It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
Cellular Respiration Definition A series of metabolic reactions that takes place within the cell is called cellular respiration. The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals birds humans and other mammals.
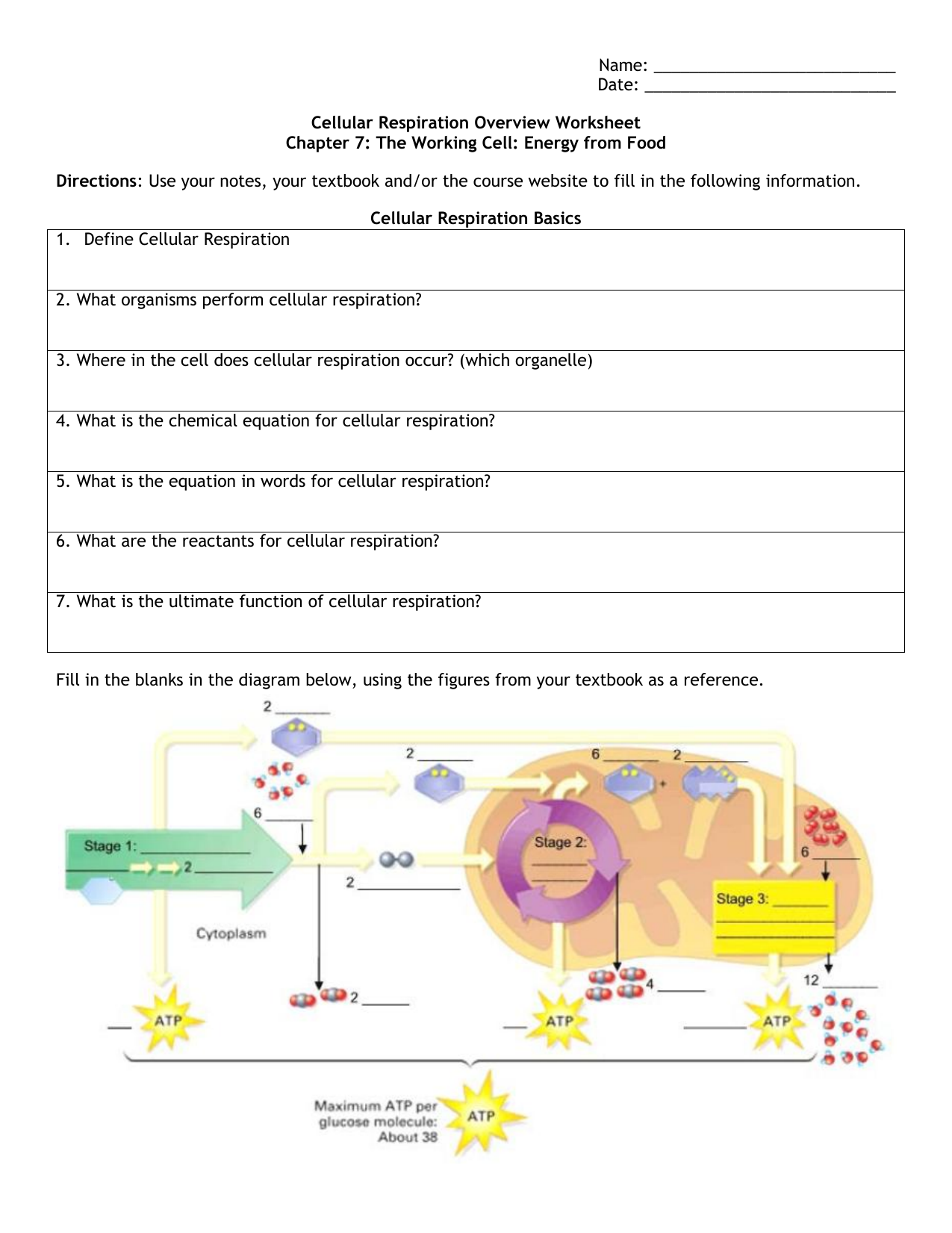
Cellular Respiration Definition Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy sugar into a usable form of energy ATP in the cell. The process involves harvesting biochemical energy from organic molecules especially glucose is converted into ATP adenosine triphosphate. Cellular respiration is a set of biochemical reactions that takes place in most cells.
It is a continuous process that takes place within the cells of animals and plants. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms. Cellular respiration is defined as the conversion of fuel into energy and nutrients within the mitochondria and cytosol of cells.
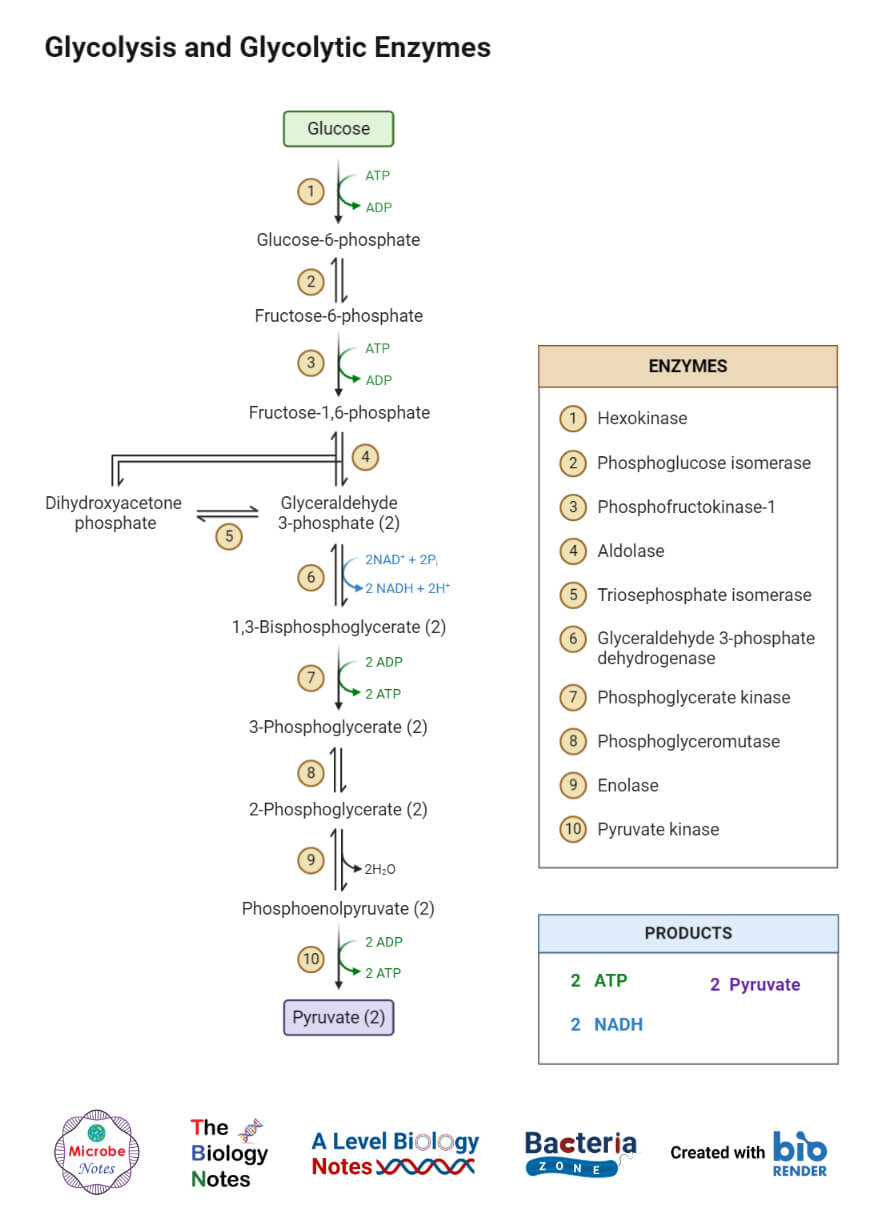
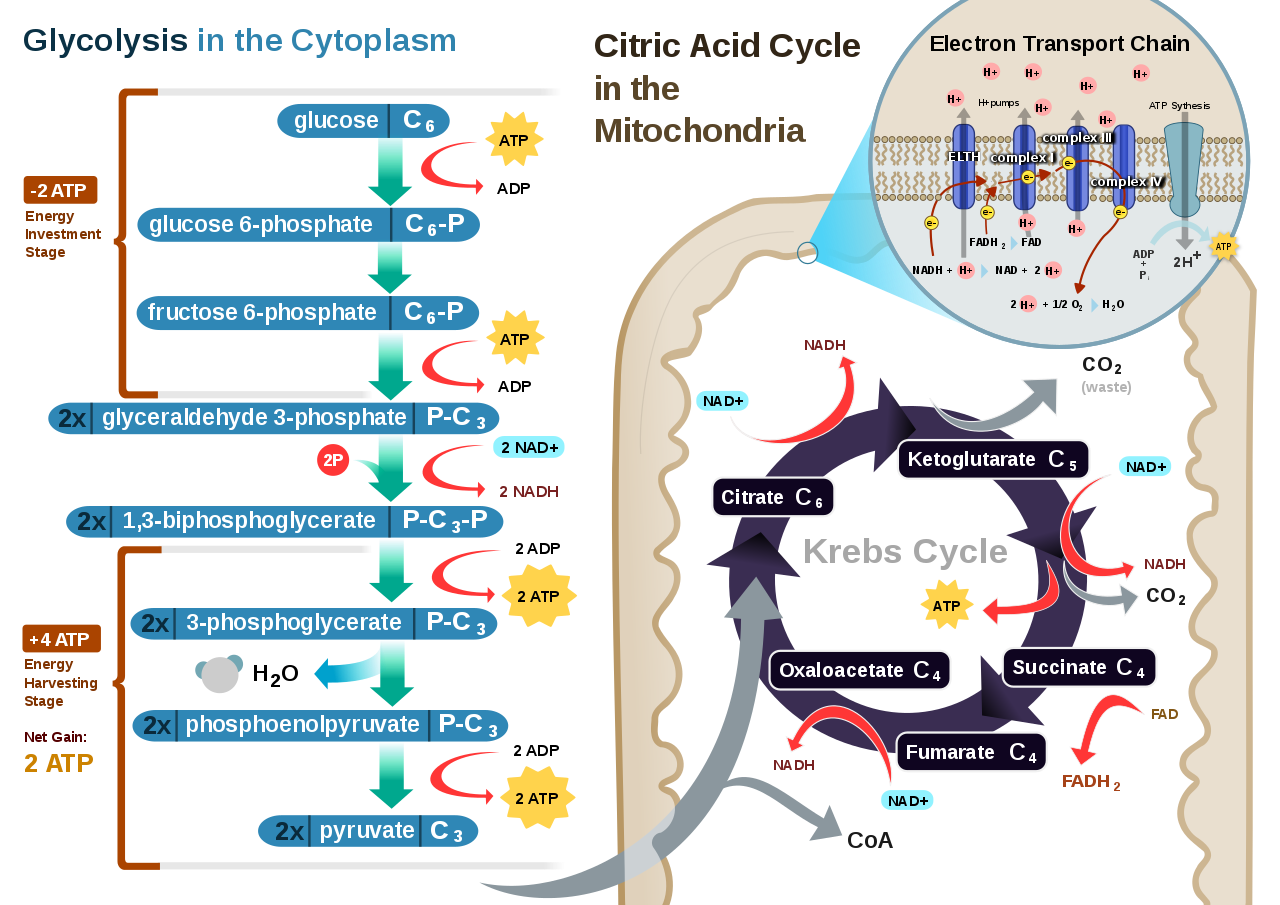
The cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into energy-coin Adenosine triphosphate ATP. Cellular Respiration aerobic C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O 32 ATP Photosynthesis 6CO2 6H2O C6H12O6 6O2 By looking at the two formulas it becomes evident that the products of one of the reactions are reactants of the other. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)